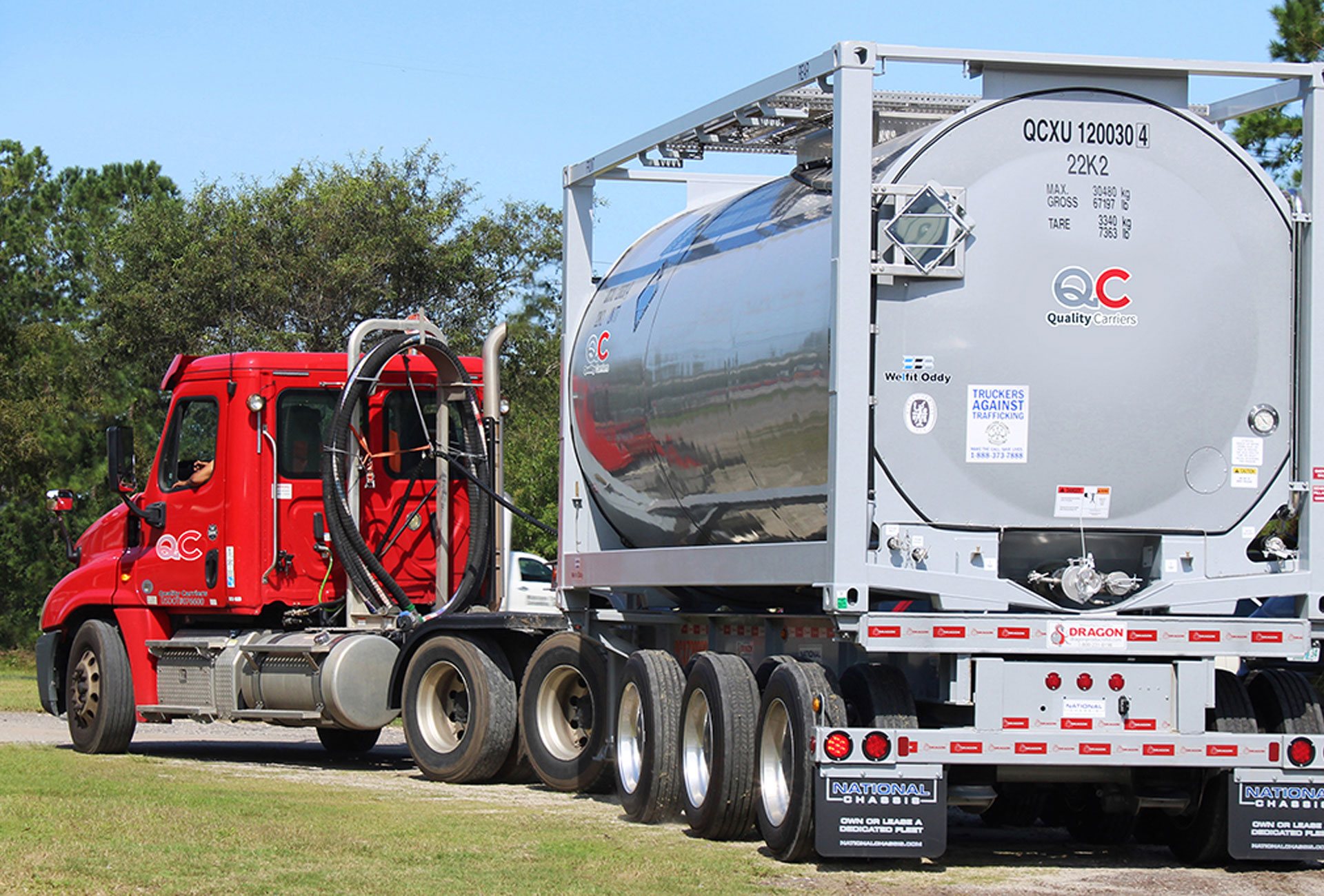
When transporting bulk hazardous and non-hazardous goods, intermodal carriers play a crucial role in ensuring the safe and efficient movement of these substances across different modes of transportation. Among the essential components of intermodal carriers are intermodal tanks, designed specifically to securely transport various substances such as chemicals, petroleum products, and food-grade materials. In this blog, we will examine what intermodal tanks look like, reading their distinct design, structure, and characteristics. Understanding the appearance and features of intermodal tanks is key to comprehending their role in the logistics and transportation industry, where these specialized containers ensure the smooth flow of vital resources worldwide.
What are intermodal tanks?
Intermodal tanks, or tank containers, are specialized containers designed for transporting bulk hazardous and non-hazardous goods. They are a crucial component of intermodal carriers, enabling the seamless transfer of substances across various modes of transportation, including rail, road, and sea. Intermodal tanks are constructed with durable materials, such as stainless steel or aluminum, to withstand the rigors of transportation and ensure the safety of the contents being carried. These containers come in various sizes and capacities, allowing for the transport of different volumes of liquids or gasses. Intermodal tanks have valves, safety devices, and internal baffles to facilitate controlled loading and unloading, maintain pressure levels, and prevent spills or leaks. Their standardized design enables efficient handling and compatibility with a wide range of transportation infrastructure, making them an essential tool for the bulk transport industry.
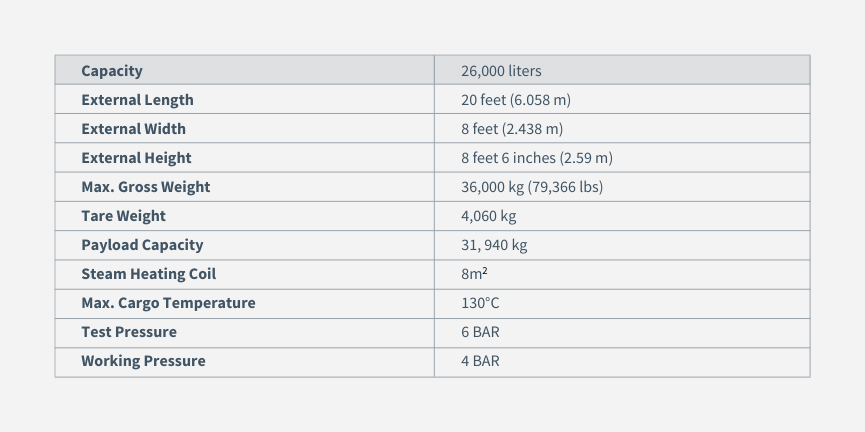
ISO Tanks Specifications
ISO tank containers are designed to transport various liquids, including explosives, chemicals, flammable substances, and even food products. These containers offer a secure and efficient means of transporting liquids, eliminating the need for transferring the product between multiple containers. They provide a cost-effective solution for liquid transportation, ensuring the integrity and safety of the cargo. The 20 ft ISO tank container is the most common among the various sizes available. It has a capacity of up to 26,000 liters, enabling the intermodal transportation of substantial volumes of liquid.
Here is an overview of the typical specifications for a standard intermodal ISO tank container:
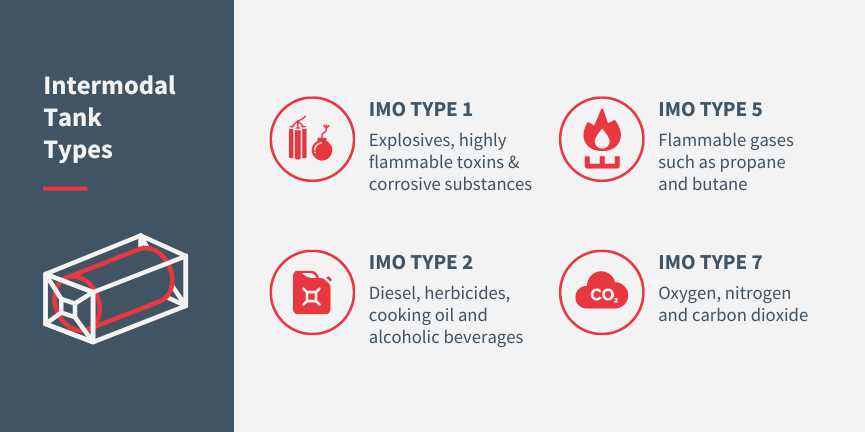
Different intermodal tank types
Tank containers are classified into three types by the International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMO): IMO Type 1, IMO Type 2, and IMO Type 5.
IMO Type 1
IMO Type 1 tank containers are designed by intermodal transportation companies to transport extremely hazardous substances or pose a high risk in terms of toxicity, reactivity, or flammability. These tanks are built with thick steel walls and are often pressure vessels capable of withstanding high pressures. They transport gases, chemicals, and other dangerous substances that require maximum containment and safety measures.
IMO Type 2
IMO Type 2 tank containers are designed to carry moderately hazardous substances with lower risks than those transported in Type 1 tanks. These tanks are also constructed with sturdy materials, such as steel or aluminum, but may require a different level of reinforcement than Type 1 tanks. They are commonly used for transporting liquids and gases that are less volatile or less reactive.
IMO Type 5
IMO Type 5 tank containers are specialized containers designed to carry cryogenic substances, such as liquefied gases, that must be maintained at extremely low temperatures. These tanks are heavily insulated and have specialized pressure control systems to keep the contents in a cryogenic state. They are typically used to transport substances like liquefied natural gas (LNG) or liquefied oxygen, requiring specific temperature and pressure conditions.
Note: In addition to the aforementioned three IMO tank types, there exists an additional classification known as IMO Type 7 tank containers. These specialized containers are designed and approved for transporting cryogenic or refrigerated liquids, including oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and similar materials. IMO Type 7 tanks are constructed to maintain the extremely low temperatures required to transport these cryogenic or refrigerated liquids safely.
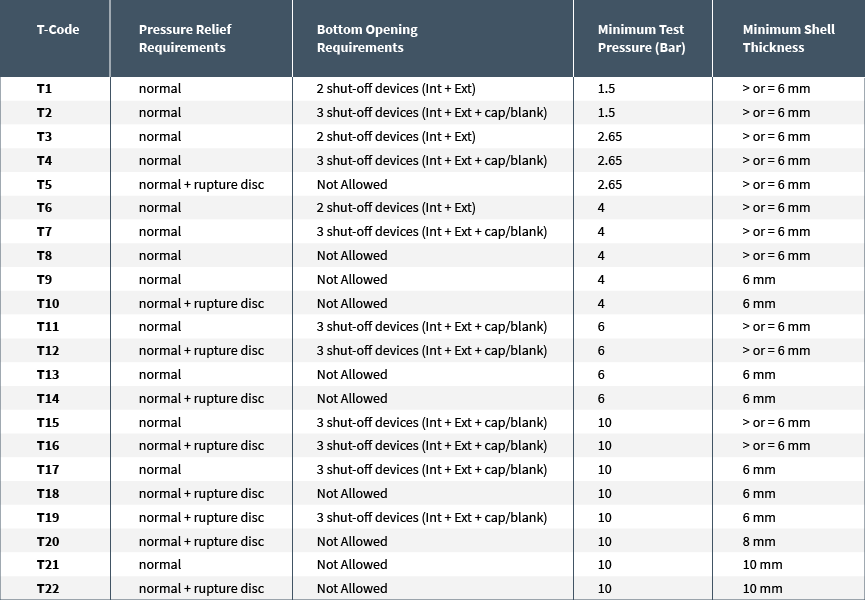
In 2001, the original IMO type classification system for tank containers was replaced by the “T” code system. It categorizes tank containers from T1 to T22 and specifies the type of cargo that each container is designed to transport.
The “T” code system classification
Advantages of Using intermodal tanks
Tank containers are a secure, dependable, and cost-efficient means of transporting bulk liquids globally. These containers undergo rigorous design, testing, and approval processes to ensure various liquid products’ safe, economical, and efficient transportation. With their emphasis on safety and efficiency, tank containers provide a reliable solution for the movement of bulk liquids, offering peace of mind to industries relying on their secure transport.
Cost Effectiveness – Intermodal tanks offer cost savings through efficient logistics planning and utilization of transportation infrastructure. The standardized dimensions of intermodal tanks allow for maximum cargo capacity, minimizing wasted space and optimizing shipping costs. Additionally, the ability to seamlessly transfer intermodal tanks between different modes of transportation reduces the need for additional handling and lowers overall transportation costs.
Efficiency in Use – Intermodal tanks provide efficient transport solutions by seamlessly integrating into various transportation modes, such as rail, road, and sea. They eliminate the need for cargo transfer between containers or vehicles, streamlining the shipping process and reducing transit times. This efficiency translates to improved supply chain operations and timely delivery of goods.
Safety – Intermodal tanks are designed with safety as a top priority. They are built to withstand the rigors of transportation and are equipped with safety features such as pressure relief valves and secure locking mechanisms. These safety measures ensure the integrity of the cargo and minimize the risk of leaks, spills, or contamination during transit. Standardized design and adherence to regulatory standards further contribute to safe handling and transport.
Convenience – Intermodal tanks offer comfort in handling and storage. They provide a single, secure container for transporting and storing bulk liquids or gases, eliminating the need for additional packaging or intermediate handling. Intermodal tanks can be easily loaded onto trucks, railcars, or ships, simplifying logistics operations and facilitating smooth transitions between transportation modes.
Storage – Intermodal tanks can also serve as temporary storage units. They offer a practical solution for storing bulk liquids or gases at a specific location, whether at a transportation hub, distribution center, or customer site. This flexibility in storage helps optimize inventory management and enables efficient distribution of goods.
Conclusion
Intermodal tanks, with their distinctive cylindrical shape, durable construction, and specialized features, are the backbone of bulk liquid and gas transport. These containers are designed to ensure the safe, efficient, and cost-effective movement of various substances across multiple modes of transportation. With their standardized dimensions and compatibility with rail, road, and sea transport, intermodal tanks provide versatility and convenience in logistics planning. Using high-quality materials and safety mechanisms guarantees the integrity and security of the cargo, while standardized labeling and markings facilitate proper handling and compliance with regulations.
Intermodal tanks optimize storage and transportation efficiency and contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and promoting efficient resource utilization. Intermodal tanks embody reliability, safety, and efficiency in the bulk liquid and gas transport industry.
FAQs
Intermodal tanks transport many substances, including chemicals, petroleum products, food-grade materials, liquefied gases, and other liquid or gaseous commodities.
Yes, intermodal tanks are designed to be compatible with multiple modes of transportation, such as rail, road, and sea. They can be seamlessly transferred between transport systems without loading and reloading the cargo.
Intermodal tanks are typically loaded and unloaded using specialized equipment such as cranes, forklifts, or loading ramps. The process may vary depending on the specific requirements of the transport infrastructure and the type of cargo being handled.
Yes, intermodal tanks are reusable. They are designed to withstand multiple trips and can be used for extended periods. After unloading, intermodal tanks are often cleaned, inspected, and prepared for the next shipment.
Yes, intermodal tanks are regulated by international standards and regulations, including those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), United Nations (UN), and various national and regional authorities. Compliance with these standards ensures the safe and proper use of intermodal tanks for bulk liquid and gas transport.




